What Is HDMI? Beginner’s Guide to the Most Common Display Standard
High-Definition Multimedia Interface, better known as HDMI, has become the backbone of how we connect our TVs, monitors, gaming consoles, and laptops today. But if you’ve ever wondered what HDMI really is and why it dominates the display world, this guide is for you. We’ll cover the basics, break down the different HDMI versions, explain the types of cables and connectors, and explore how HDMI stacks up against other display standards. By the end, you’ll know exactly which HDMI setup works best for your needs.

What Is HDMI? Understanding the Basics
HDMI Definition
HDMI stands for High-Definition Multimedia Interface. It is a digital interface standard designed to transmit both high-definition video and multi-channel audio over a single cable. Unlike older standards such as VGA or DVI, HDMI consolidates multiple signal types into one convenient connection, making it the go-to solution for home entertainment and professional setups.
Why HDMI Became the Standard
When HDMI was introduced in 2003, it quickly replaced older analog technologies. VGA required separate audio cables, and DVI lacked audio support entirely. HDMI’s ability to transmit crystal-clear video and up to 8 channels of audio revolutionized consumer electronics. According to industry data, more than 10 billion HDMI-enabled devices have been shipped worldwide, making it the most widely adopted display standard today.
How HDMI Works
HDMI transfers uncompressed digital signals, which means there is no loss of quality between the source device and the display. When you connect your Blu-ray player or gaming console to a TV with HDMI, the signal is carried digitally—ensuring sharper video and richer sound compared to analog alternatives.

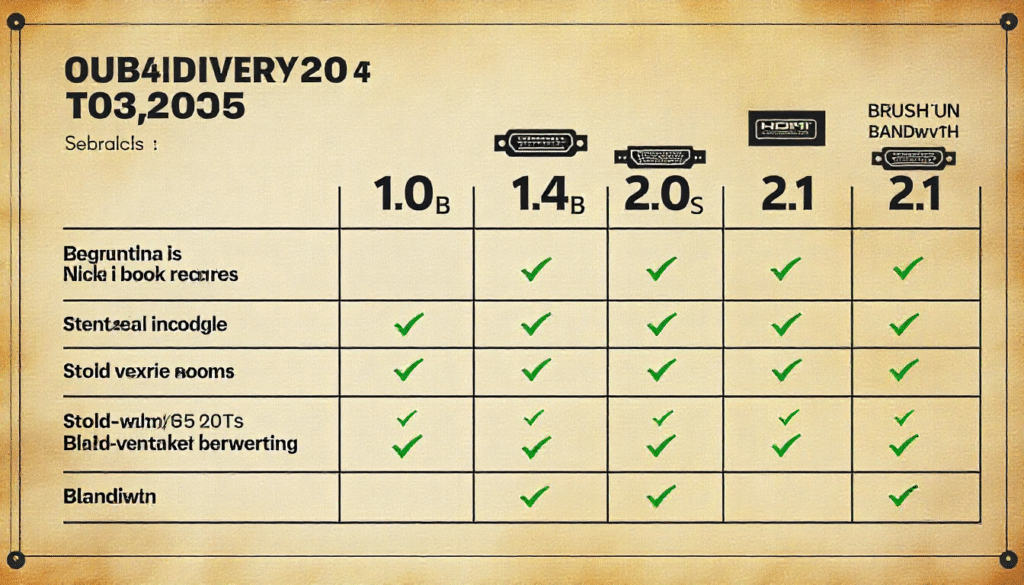
HDMI Versions Explained (From 1.0 to 2.1)
HDMI 1.0 – The Beginning
The first HDMI specification (1.0) launched in 2003 and supported 1080p resolution with up to 8 channels of audio. At the time, this was a major improvement over analog connectors.
HDMI 1.4 – Enter 3D and 4K
In 2009, HDMI 1.4 introduced support for 3D video and 4K resolution (at 30Hz). It also added HDMI Ethernet Channel (HEC), allowing compatible devices to share an internet connection.
HDMI 2.0 – True 4K Revolution
Released in 2013, HDMI 2.0 was a game-changer for 4K content. It supported 4K at 60Hz, HDR (High Dynamic Range), and expanded color spaces. This made it perfect for UHD TVs and gaming consoles like the PlayStation 4 Pro.
HDMI 2.1 – The Future of Gaming and 8K
HDMI 2.1, launched in 2017, supports resolutions up to 8K at 60Hz and 4K at 120Hz. It introduced Variable Refresh Rate (VRR) and Auto Low Latency Mode (ALLM), which are essential for next-generation gaming consoles like the PlayStation 5 and Xbox Series X.
HDMI Cables and Connectors You Should Know
HDMI Cable Types
Not all HDMI cables are created equal. The main categories include:
- Standard HDMI – Up to 1080i/720p.
- High-Speed HDMI – Supports 1080p and 4K (30Hz).
- Premium High-Speed HDMI – Designed for 4K HDR at 60Hz.
- Ultra High-Speed HDMI – Required for 8K and HDMI 2.1 features.
HDMI Connector Types
There are several connector types to fit different devices:
- Type A (Standard HDMI) – Used in TVs, monitors, and consoles.
- Type C (Mini HDMI) – Common in tablets and cameras.
- Type D (Micro HDMI) – Found in small portable devices.
Do Expensive HDMI Cables Matter?
A common misconception is that pricey HDMI cables deliver better video quality. In reality, HDMI transmits digital signals—so a $10 cable performs the same as a $100 one if it meets the required specification. Cable length and build quality matter more than price.
Common Uses of HDMI in Daily Life
HDMI in Home Entertainment
HDMI is essential in home theaters. From smart TVs and Blu-ray players to soundbars and AV receivers, HDMI ensures that your audio and video signals remain crystal clear.
HDMI for Gaming
Modern gaming consoles like the PlayStation 5 and Xbox Series X rely on HDMI 2.1 to deliver 4K at 120Hz with VRR. Gamers benefit from smoother motion, reduced lag, and immersive HDR visuals.
HDMI in Computers and Office Use
Laptops, desktop PCs, and projectors commonly use HDMI for quick plug-and-play connectivity. HDMI ensures seamless presentations in classrooms, offices, and conference rooms.

HDMI vs Other Display Standards
HDMI vs DisplayPort
While HDMI is more common in consumer electronics, DisplayPort often appeals to PC gamers and professionals. DisplayPort offers higher bandwidth for multi-monitor setups and adaptive sync technologies.
HDMI vs VGA/DVI
VGA is an analog standard, and DVI, though digital, is limited in resolution and lacks audio support. HDMI’s digital transmission, wide compatibility, and audio integration make it the superior choice for most users.
When to Choose HDMI
For everyday entertainment and office use, HDMI remains the most convenient and universal option. DisplayPort is excellent for high-end gaming or multi-display productivity setups, but HDMI dominates TVs and consumer devices.
The Future of HDMI and What to Expect
Looking ahead, HDMI will continue to evolve alongside display technologies. With 8K TVs entering the mainstream and VR/AR applications demanding ultra-low latency, HDMI’s bandwidth and feature set will expand further. HDMI 2.1 already provides a strong foundation for the next decade of entertainment and gaming.
Conclusion: Why HDMI Still Matters
HDMI has proven itself as the most common and versatile display standard. From home theaters and gaming consoles to laptops and projectors, HDMI simplifies connectivity with just one cable for both video and audio. As technology advances into 8K and beyond, HDMI will remain a cornerstone of digital entertainment and productivity.
Next Steps: Check which HDMI version your devices support, and consider upgrading your cable if you want to unlock 4K HDR or 8K gaming. For a deeper dive into HDMI vs DisplayPort and which one fits your needs, don’t miss our complete guide: DisplayPort vs HDMI: Which One Should You Choose in 2025?.


Leave a Reply